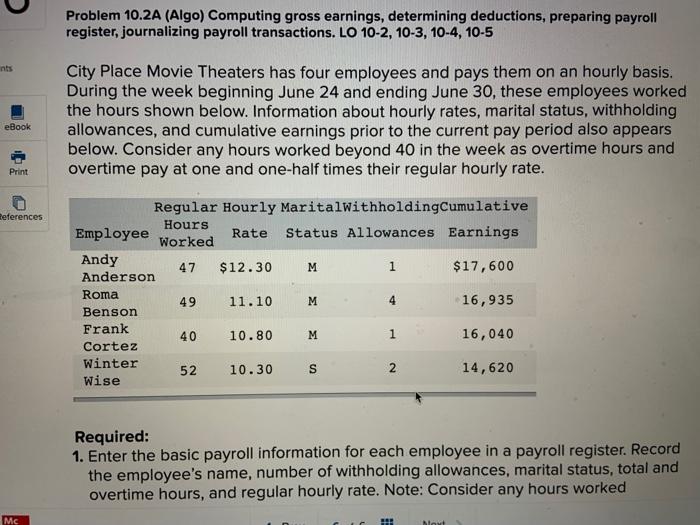
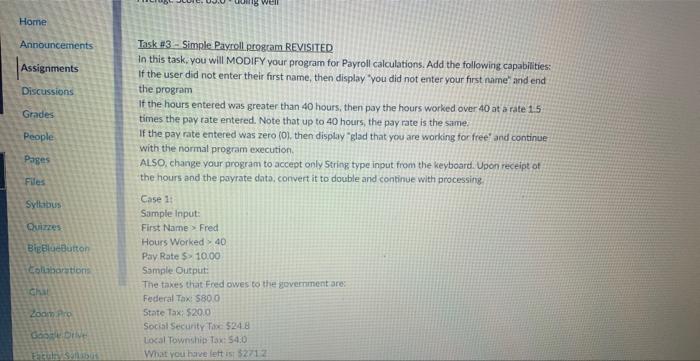
Problem 12-8 Preparing the Payroll embarks us on an enlightening journey through the intricacies of payroll processing. This detailed guide delves into the essential steps, calculations, and considerations involved in ensuring accurate and timely payroll preparation.
From gathering employee data to calculating gross pay, navigating deductions and withholdings, and understanding net pay calculation, this comprehensive resource provides a thorough understanding of the payroll process.
Understanding the Payroll Process
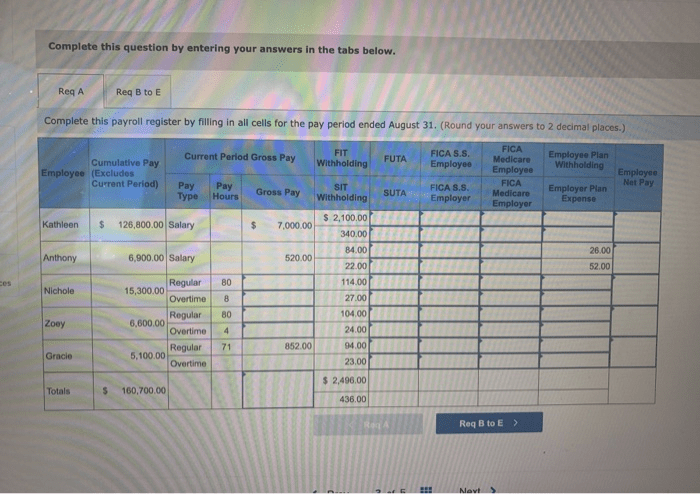
The payroll process involves a series of critical steps to ensure accurate and timely payment of employee compensation. It encompasses data collection, calculation of gross pay, deductions and withholdings, net pay calculation, record-keeping, and compliance with payroll regulations.
Collecting Employee Data
Payroll processing requires the collection of various employee data, including:
- Personal information (e.g., name, address, contact details)
- Tax information (e.g., Social Security number, withholding allowances)
- Time and attendance records (e.g., hours worked, overtime)
- Benefits enrollment information (e.g., health insurance, retirement plans)
Calculating Gross Pay
Gross pay represents the total amount of compensation earned by an employee before any deductions or withholdings are applied. It typically includes:
- Wages or salaries
- Bonuses
- Overtime pay
- Commissions
Deductions and Withholdings
Various deductions and withholdings are made from gross pay to fulfill legal obligations and provide employee benefits. Common deductions include:
- Federal income tax
- Social Security tax
- Medicare tax
- State income tax (if applicable)
- Health insurance premiums
- Retirement plan contributions
Net Pay Calculation
Net pay is the amount of compensation that an employee receives after all deductions and withholdings have been applied. It is calculated using the following formula:
Gross Pay
- Deductions
- Withholdings = Net Pay
Preparing Payroll Records
Accurate and complete payroll records are essential for maintaining compliance and providing employees with a clear understanding of their compensation. Common payroll records include:
- Pay stubs
- Payroll registers
- Payroll summaries
Payroll Reporting and Compliance, Problem 12-8 preparing the payroll
Payroll professionals must comply with various reporting requirements imposed by government agencies, including:
- Filing payroll tax returns (e.g., Form 941, Form W-2)
- Submitting employee wage information (e.g., Form W-4)
- Meeting deadlines and adhering to regulations set by the IRS, Social Security Administration, and other relevant agencies
FAQ Summary: Problem 12-8 Preparing The Payroll
What are the key steps involved in preparing a payroll?
The key steps include collecting employee data, calculating gross pay, applying deductions and withholdings, calculating net pay, and preparing payroll records.
What types of employee data are needed for payroll processing?
Employee data typically includes name, address, social security number, pay rate, and tax withholding information.
How is gross pay calculated?
Gross pay is calculated by multiplying the employee’s pay rate by the hours worked, and adding any bonuses or overtime pay.
What are common deductions and withholdings from gross pay?
Common deductions include health insurance premiums, retirement contributions, and union dues. Withholdings include federal and state income taxes, and social security taxes.
How is net pay calculated?
Net pay is calculated by subtracting deductions and withholdings from gross pay.