Cell defense the plasma membrane answer key page 2 – Embark on an exploration of cell defense mechanisms, with a focus on the crucial role of the plasma membrane. This comprehensive guide, “Cell Defense: The Plasma Membrane Answer Key Page 2,” provides an in-depth understanding of how cells protect themselves from external threats, ensuring their survival and optimal functioning.
Delve into the intricate structure and functions of the plasma membrane, the gatekeeper of the cell. Discover how it regulates the entry and exit of substances, maintaining cellular homeostasis. Explore the mechanisms of phagocytosis and endocytosis, the processes by which cells engulf and internalize foreign particles.
1. Introduction
The cell defense system is a complex network of mechanisms that protect cells from damage and infection. The plasma membrane, which surrounds the cell, plays a crucial role in this defense system.
2. Structure and Function of the Plasma Membrane: Cell Defense The Plasma Membrane Answer Key Page 2
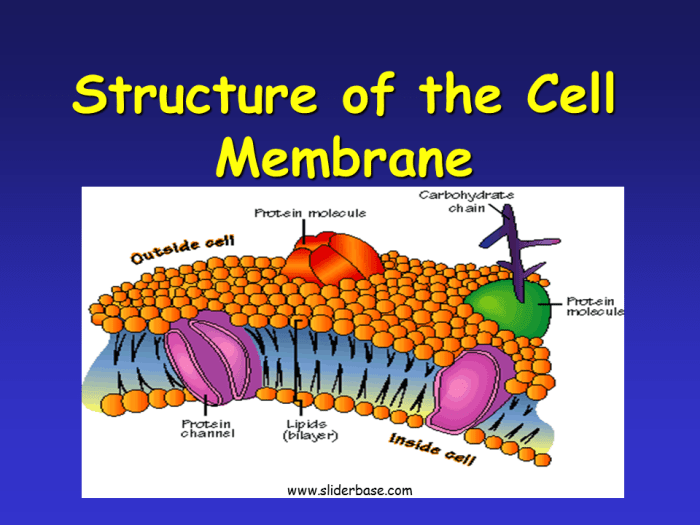
The plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. The phospholipids are arranged in a head-to-tail orientation, with the hydrophilic heads facing outward and the hydrophobic tails facing inward. The proteins are embedded in the lipid bilayer and can span the entire membrane or just part of it.
The plasma membrane has several important functions, including:
- Regulating the movement of molecules into and out of the cell
- Protecting the cell from damage
- Communicating with other cells
2.1. Regulating Cell Entry and Exit, Cell defense the plasma membrane answer key page 2
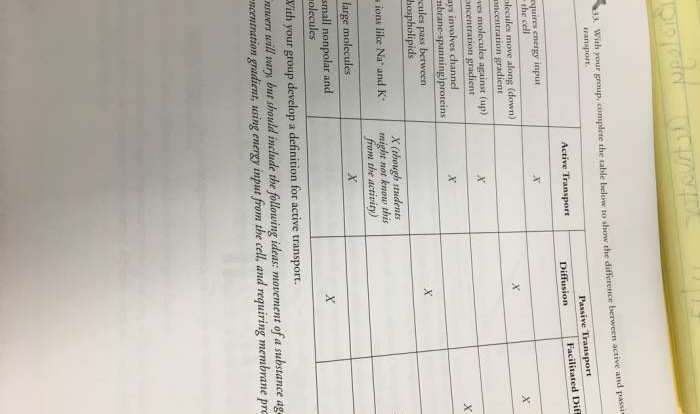
The plasma membrane regulates the movement of molecules into and out of the cell through a variety of mechanisms, including:
- Simple diffusion: The movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
- Facilitated diffusion: The movement of molecules across a membrane with the help of a carrier protein
- Active transport: The movement of molecules across a membrane against a concentration gradient, requiring energy
- Endocytosis: The process by which cells take in molecules by engulfing them with their plasma membrane
- Exocytosis: The process by which cells release molecules by fusing their plasma membrane with the membrane of a vesicle
Helpful Answers
What is the primary function of the plasma membrane in cell defense?
The plasma membrane acts as a barrier, regulating the entry and exit of substances into and out of the cell, protecting it from harmful external agents.
How do cells recognize and respond to foreign invaders?
Cell surface receptors play a crucial role in recognizing foreign particles, triggering phagocytosis or endocytosis to engulf and internalize them.
What is the significance of antimicrobial peptides in cell defense?
Antimicrobial peptides are potent molecules that directly attack and destroy microorganisms, providing an additional layer of protection against infection.