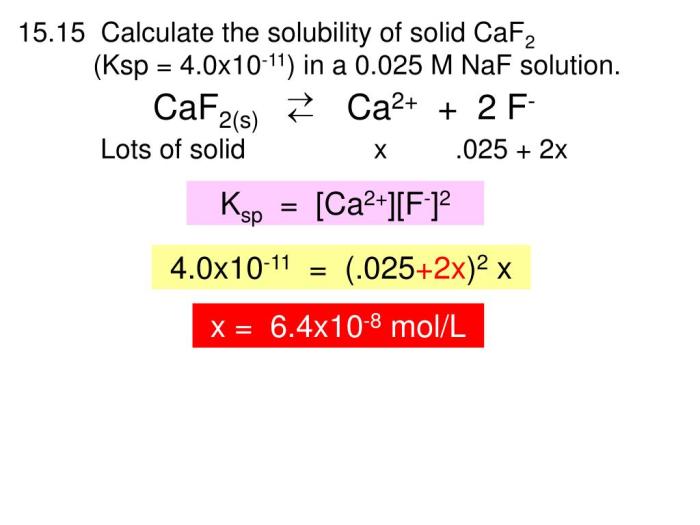
Complete the following solubility constant expression for CaF2: a journey into the intricate world of chemistry, where we unravel the mysteries of solubility constants and their profound implications. This comprehensive guide delves into the depths of CaF2’s solubility constant expression, exploring its significance, influencing factors, and practical applications.
As we embark on this scientific expedition, we will encounter the fundamental principles of solubility constants, deciphering their role in understanding the behavior of chemical compounds in aqueous solutions. Through a meticulous examination of CaF2’s solubility constant expression, we will gain invaluable insights into the factors that govern the solubility of ionic compounds and their interactions with their surrounding environment.
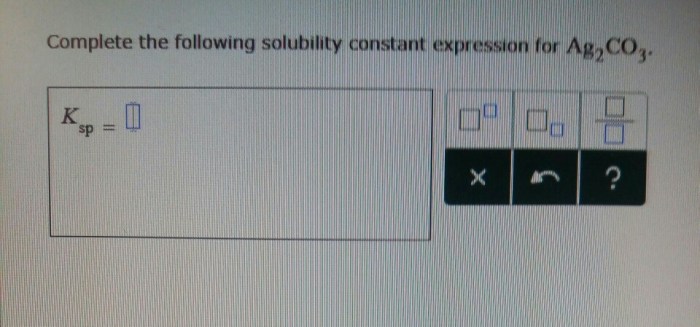
Solubility Constant
A solubility constant, often denoted as K sp, is a quantitative measure of the extent to which a sparingly soluble ionic compound dissolves in water. It is an equilibrium constant that represents the product of the molar concentrations of the constituent ions raised to their respective stoichiometric coefficients in a saturated solution.
Solubility Constant Expression for CaF2: Complete The Following Solubility Constant Expression For Caf2

The solubility constant expression for calcium fluoride (CaF 2) is:
Ksp= [Ca 2+][F –] 2
where:
- [Ca 2+] is the molar concentration of calcium ions in the saturated solution
- [F –] is the molar concentration of fluoride ions in the saturated solution
Factors Affecting Solubility Constant
The solubility constant of a compound can be affected by several factors, including:
- Temperature:The solubility constant generally increases with increasing temperature.
- Pressure:The solubility constant is not significantly affected by pressure for most ionic compounds.
- Ionic strength:The solubility constant decreases with increasing ionic strength of the solution.
Applications of Solubility Constant
Solubility constants have various practical applications in fields such as:
- Chemistry:Predicting the solubility and precipitation of ionic compounds.
- Environmental science:Assessing the solubility and potential environmental impact of pollutants.
- Pharmacology:Designing drugs with specific solubility properties.
Experimental Determination of Solubility Constant
The solubility constant can be experimentally determined by measuring the concentration of the dissolved ions in a saturated solution. This can be done using techniques such as:
- Gravimetric analysis:Measuring the mass of the precipitate formed after a known amount of the compound is dissolved.
- Conductivity measurements:Measuring the electrical conductivity of the saturated solution.
Comparison of Solubility Constants
| Compound | Ksp (25 °C) |
|---|---|
| CaF2 | 3.2 × 10-11 |
| BaSO4 | 1.1 × 10-10 |
| AgCl | 1.8 × 10-10 |
Applications of Solubility Constants in Chemical Calculations, Complete the following solubility constant expression for caf2
Solubility constants can be used to solve various chemical problems, such as:
- Calculating the solubility of a compound:Using the K spand the stoichiometry of the dissolution reaction.
- Predicting the precipitation of a compound:By comparing the ion product (IP) to the K sp.
FAQ Guide
What is the significance of solubility constants?
Solubility constants play a crucial role in predicting the solubility of compounds in aqueous solutions. They provide quantitative information about the extent to which a compound dissolves, allowing scientists to understand the behavior of chemical species in various environments.
How can the solubility constant expression for CaF2 be used in practice?
The solubility constant expression for CaF2 finds applications in diverse fields. For instance, in environmental science, it helps assess the solubility of fluoride ions in natural waters, influencing decisions related to water quality management. In pharmaceutical development, it aids in designing drug formulations with controlled solubility profiles.